|
 |
 |
 |
--- Page 7 --- |
 |
|
"CLICK"
below image; or, |
|
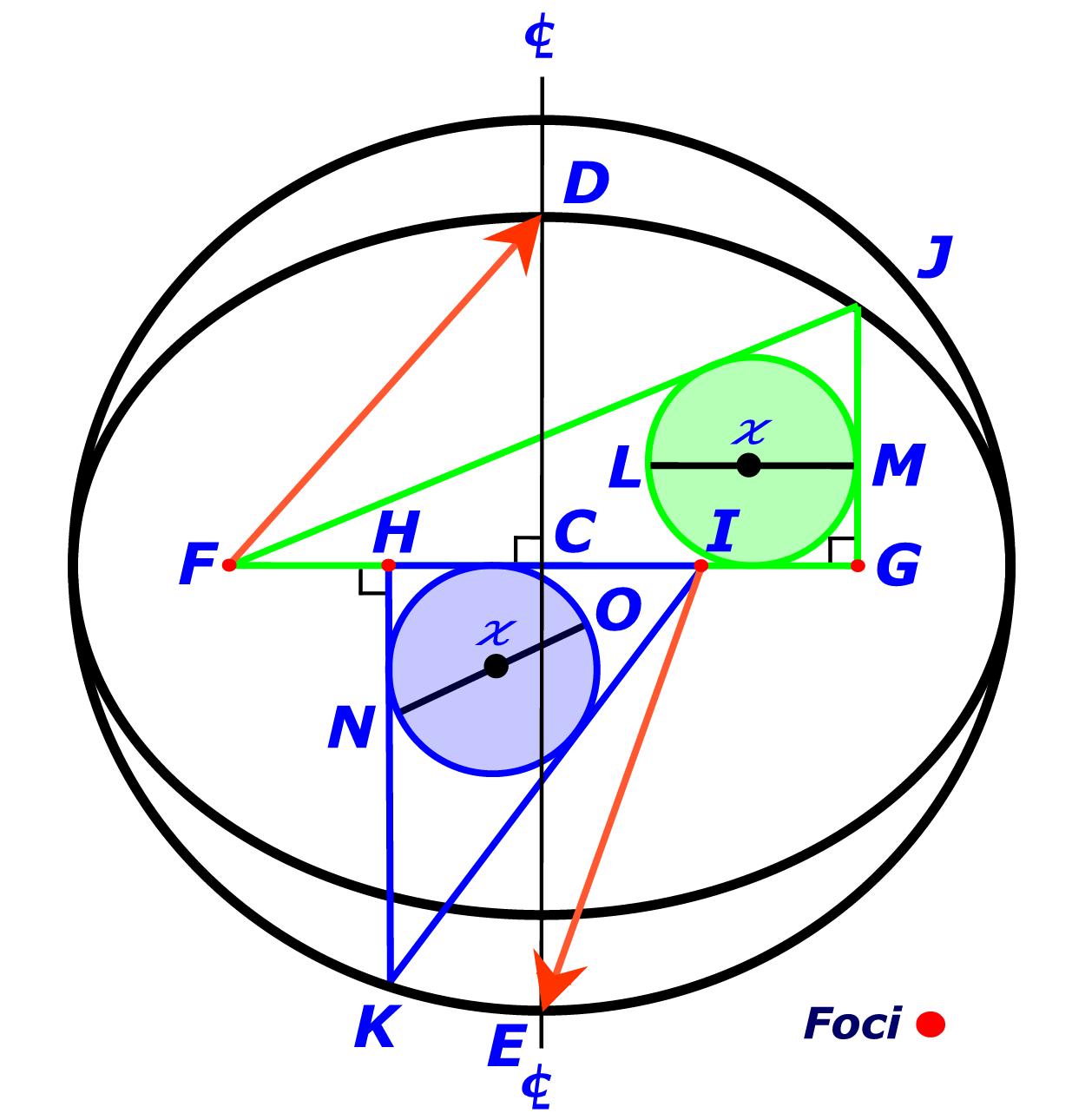
Emergent Ellipse Geometry Pythagorean Triangle Pairs (PTP) |
 |
|
|
|
Extend the Center Line as required Draw a Vector Line EI that is equal to Line GH from Point I to the Center Line. Draw a Vector Line DF that is equal to Line FI from Point F to the Center Line. |
 |
 |
|
Transpose Pythagorean Triangles FGJ and HIK as indicated. Extend the Center Line as required. |
|
Inscribe Circles (in-circles) FGJ and HIK with centers at  and respective diameters LM and NO. Bisect Lines FG and HI with Center Lines. |
 |
 |
|
Construct a paired Pythagorean Triangle FGJ in accordance with base, side, and hypotenuse as indicated in the below Table of Formulas. A pair of Pythagorean Triangles have short sides, radius (r) and base (b), which vary by the Elliptical Constant (EC) = |
 |
 |
|
Construct a Pythagorean Triangle
HIK in accordance with base, side, and hypotenuse as indicated in the below Table of Formulas. Pythagorean Triangles are triangles with a right angle; and, all sides that are integers. |
|
|
Amazingly, the diameters of both circles inscribed within each different Pythagorean Triangle, of a given pair, are even integers, that are . . . identical to one another. Thus, the radii of the inscribed circles are also equal integers. |
|
 |
One must
continuously ask: Why? Why? Why?; and, Why? again. And, realize that Fundamental Nature is the source of all Mathematics! |
| Summary | Epsilon equals One | Proof of One | Inverse Square Law | Elliptical Constant | Duality of Infinity |
| Natural Function | Brunardot Theorem |
revised Fibonacci Sequence |
Challenge to Academe | Pulsoid Theorem | Fundamental Intrinsic Time |
| Salient Structural Parts | Universal Locus | Antimatter | Heaven/God/Hell | Philogic | Entanglement |