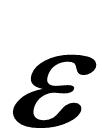|
 |
 |
 |
--- Page 2 --- |
 |
|
"CLICK"
below image; or, |
 |
 |
|
Construct a paired Pythagorean Triangle FGJ in accordance with base, side, and hypotenuse as indicated in the below Table of Formulas. A pair of Pythagorean Triangles have short sides, radius (r) and base (b), which vary by the Elliptical Constant (EC) = |
 |
 |
|
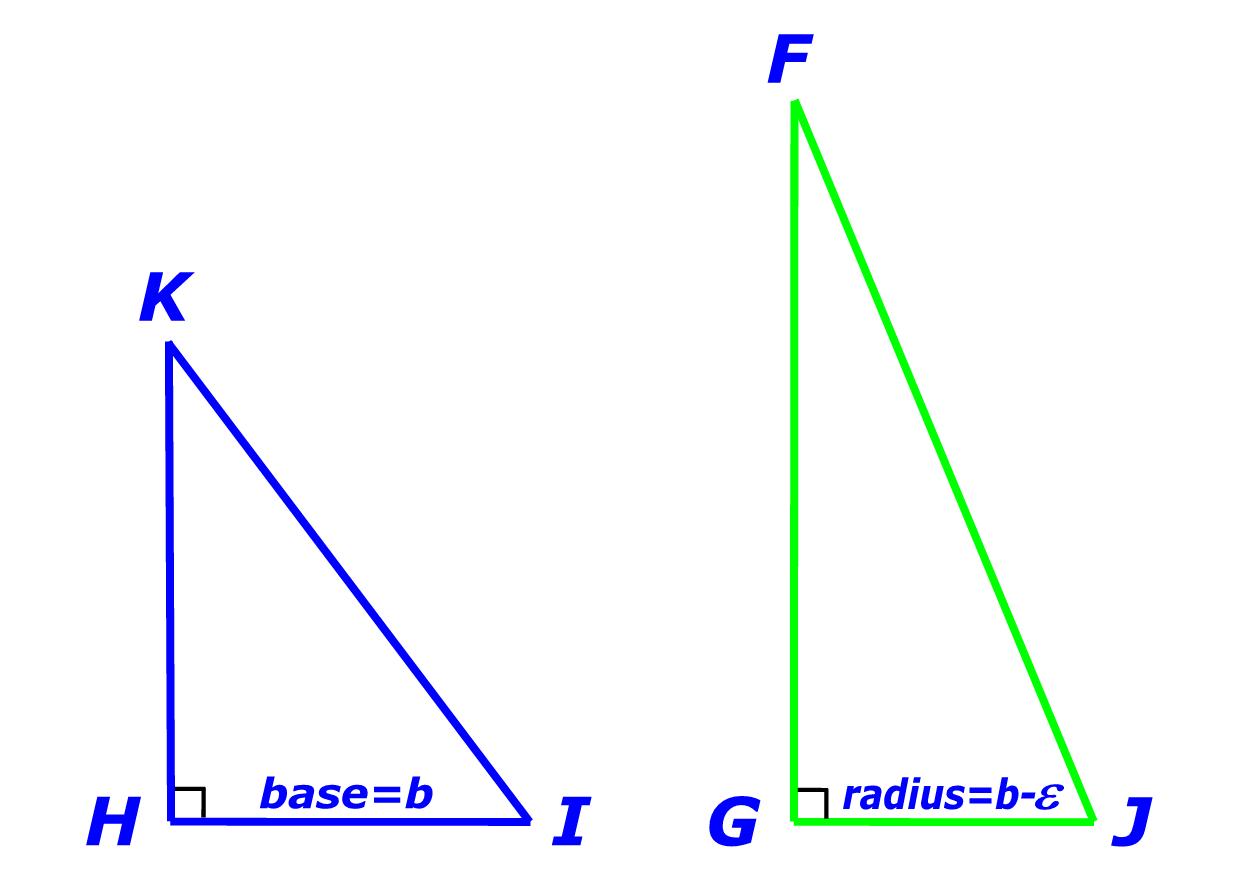
Construct a Pythagorean Triangle
HIK in accordance with base, side, and hypotenuse as indicated in the below Table of Formulas. Pythagorean Triangles are triangles with a right angle; and, all sides that are integers. |
|
A Pythagorean Triangle Pair (PTP) can be mapped to every integer greater than One. Four angles (two of the six angles are right angles) and all six sides of a Pythagorean Triangle Pair are of unlike values. |
|
 |
One must
continuously ask: Why? Why? Why?; and, Why? again. And, realize that Fundamental Nature is the source of all Mathematics! |
| Summary | Epsilon equals One | Proof of One | Inverse Square Law | Elliptical Constant | Duality of Infinity |
| Natural Function | Brunardot Theorem |
revised Fibonacci Sequence |
Challenge to Academe | Pulsoid Theorem | Fundamental Intrinsic Time |
| Salient Structural Parts | Universal Locus | Antimatter | Heaven/God/Hell | Philogic | Entanglement |